Chukwa Administration Guide
Purpose
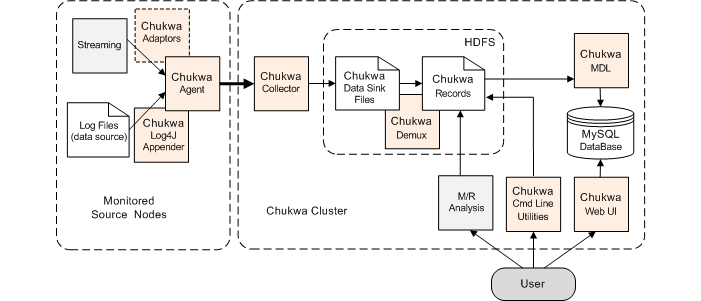
Chukwa is a system for large-scale reliable log collection and processing with Hadoop. The Chukwa design overview discusses the overall architecture of Chukwa. You should read that document before this one. The purpose of this document is to help you install and configure Chukwa.
Pre-requisites
Chukwa should work on any POSIX platform, but GNU/Linux is the only production platform that has been tested extensively. Chukwa has also been used successfully on Mac OS X, which several members of the Chukwa team use for development.
The only absolute software requirements are Java 1.6 or better and Hadoop 0.18+. HICC, the Chukwa visualization interface, requires MySQL 5.1.30+.
The Chukwa cluster management scripts rely on ssh; these scripts, however, are not required if you have some alternate mechanism for starting and stopping daemons.
Installing Chukwa
A minimal Chukwa deployment has three components:
- A Hadoop cluster on which Chukwa will store data (referred to as the Chukwa cluster).
- A collector process, that writes collected data to HDFS, the Hadoop file system.
- One or more agent processes, that send monitoring data to the collector. The nodes with active agent processes are referred to as the monitored source nodes.
In addition, you may wish to run the Chukwa Demux jobs, which parse collected data, or HICC, the Chukwa visualization tool.
First Steps
- Obtain a copy of Chukwa. You can find the latest release on the Chukwa release page.
- Un-tar the release, via tar xzf.
- Make sure a copy of Chukwa is available on each node being monitored, and on each node that will run a collector.
- We refer to the directory containing Chukwa as CHUKWA_HOME. It may be helpful to set CHUKWA_HOME explicitly in your environment, but Chukwa does not require that you do so.
General Configuration
Agents and collectors are configured differently, but part of the process is common to both.
- Make sure that JAVA_HOME is set correctly and points to a Java 1.6 JRE. It's generally best to set this in conf/chukwa-env.sh.
- In conf/chukwa-env.sh, set CHUKWA_LOG_DIR and CHUKWA_PID_DIR to the directories where Chukwa should store its console logs and pid files. The pid directory must not be shared between different Chukwa instances: it should be local, not NFS-mounted.
- Optionally, set CHUKWA_IDENT_STRING. This string is used to name Chukwa's own console log files.
Agents
Agents are the Chukwa processes that actually produce data. This section describes how to configure and run them. More details are available in the Agent configuration guide.
Configuration
This section describes how to set up the agent process on the source nodes.
The one mandatory configuration step is to set up $CHUKWA_HOME/conf/collectors. This file should contain a list of hosts that will run Chukwa collectors. Agents will pick a random collector from this list to try sending to, and will fail-over to another listed collector on error. The file should look something like:
http://<collector1HostName>:<collector1Port>/ http://<collector2HostName>:<collector2Port>/ http://<collector3HostName>:<collector3Port>/
Edit the CHUKWA_HOME/conf/initial_adaptors configuration file. This is where you tell Chukwa what log files to monitor. See the adaptor configuration guide for a list of available adaptors.
There are a number of optional settings in $CHUKWA_HOME/conf/chukwa-agent-conf.xml:
- The most important of these is the cluster/group name that identifies the
monitored source nodes. This value is stored in each Chunk of collected data;
you can therefore use it to distinguish data coming from different groups of
machines.
<property> <name>chukwaAgent.tags</name> <value>cluster="demo"</value> <description>The cluster's name for this agent</description> </property> - Another important option is chukwaAgent.checkpoint.dir. This is the directory Chukwa will use for its periodic checkpoints of running adaptors. It must not be a shared directory; use a local, not NFS-mount, directory.
Starting, stopping, and monitoring
To run an agent process on a single node, use bin/agent.sh.
Typically, agents run as daemons. The script bin/start-agents.sh will ssh to each machine listed in conf/agents and start an agent, running in the background. The script bin/stop-agents.sh does the reverse.
You can, of course, use any other daemon-management system you like. For instance, tools/init.d includes init scripts for running Chukwa agents.
To check if an agent is working properly, you can telnet to the control port (9093 by default) and hit "enter". You will get a status message if the agent is running normally.
Configuring Hadoop for monitoring
One of the key goals for Chukwa is to collect logs from Hadoop clusters. This section describes how to configure Hadoop to send its logs to Chukwa. Note that these directions require Hadoop 0.20.0+. Earlier versions of Hadoop do not have the hooks that Chukwa requires in order to grab MapReduce job logs.
The Hadoop configuration files are located in HADOOP_HOME/conf. To setup Chukwa to collect logs from Hadoop, you need to change some of the Hadoop configuration files.
- Copy CHUKWA_HOME/conf/hadoop-log4j.properties file to HADOOP_HOME/conf/log4j.properties
- Copy CHUKWA_HOME/conf/hadoop-metrics.properties file to HADOOP_HOME/conf/hadoop-metrics.properties
- Edit HADOOP_HOME/conf/hadoop-metrics.properties file and change @CHUKWA_LOG_DIR@ to your actual CHUKWA log dirctory (ie, CHUKWA_HOME/var/log)
Collectors
This section describes how to set up the Chukwa collectors. For more details, see the collector configuration guide.
Configuration
First, edit $CHUKWA_HOME/conf/chukwa-env.sh In addition to the general directions given above, you should set HADOOP_HOME. This should be the Hadoop deployment Chukwa will use to store collected data. You will get a version mismatch error if this is configured incorrectly.
Next, edit $CHUKWA_HOME/conf/chukwa-collector-conf.xml. The one mandatory configuration parameter is writer.hdfs.filesystem. This should be set to the HDFS root URL on which Chukwa will store data. Various optional configuration options are described in the collector configuration guide and in the collector configuration file itself.
Starting, stopping, and monitoring
To run a collector process on a single node, use bin/jettyCollector.sh.
Typically, collectors run as daemons. The script bin/start-collectors.sh will ssh to each collector listed in conf/collectors and start a collector, running in the background. The script bin/stop-collectors.sh does the reverse.
You can, of course, use any other daemon-management system you like. For instance, tools/init.d includes init scripts for running Chukwa collectors.
To check if a collector is working properly, you can simply access http://collectorhost:collectorport/chukwa?ping=true with a web browser. If the collector is running, you should see a status page with a handful of statistics.
Demux and HICC
Start the Chukwa Processes
The Chukwa startup scripts are located in the CHUKWA_HOME/tools/init.d directory.
- Start the Chukwa data processors script (execute this command only on the data processor node):
CHUKWA_HOME/tools/init.d/chukwa-data-processors start
- Create down sampling daily cron job:
CHUKWA_HOME/bin/downSampling.sh --config <path to chukwa conf> -n add
Set Up the Database
Set up and configure the MySQL database.
Install MySQL
Download MySQL 5.1 from the MySQL site.
tar fxvz mysql-*.tar.gz -C $CHUKWA_HOME/opt cd $CHUKWA_HOME/opt/mysql-*
Configure and then copy the my.cnf file to the CHUKWA_HOME/opt/mysql-* directory:
./scripts/mysql_install_db ./bin/mysqld_safe& ./bin/mysqladmin -u root create <clustername> ./bin/mysql -u root <clustername> < $CHUKWA_HOME/conf/database_create_table
Edit the CHUKWA_HOME/conf/jdbc.conf configuration file.
Set the clustername to the MYSQL root URL:
<clustername>=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/<clustername>?user=root
Download the MySQL Connector/J 5.1 from the MySQL site, and place the jar file in $CHUKWA_HOME/lib.
Set Up MySQL for Replication
Start the MySQL shell:
mysql -u root -p Enter password:
From the MySQL shell, enter these commands (replace <username> and <password> with actual values):
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Set Up HICC
The Hadoop Infrastructure Care Center (HICC) is the Chukwa web user interface. To set up HICC, do the following:
- Download apache-tomcat 6.0.18+ from Apache Tomcat and decompress the tarball to CHUKWA_HOME/opt.
- Copy CHUKWA_HOME/hicc.war to apache-tomcat-6.0.18/webapps.
- Start up HICC by running:
$CHUKWA_HOME/bin/hicc.sh start
- Point your favorite browser to: http://<server>:8080/hicc
Troubleshooting Tips
UNIX Processes For Chukwa Agents
The Chukwa agent process name is identified by:
- org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.datacollection.agent.ChukwaAgent
Command line to use to search for the process name:
- ps ax | grep org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.datacollection.agent.ChukwaAgent
UNIX Processes For Chukwa Collectors
Chukwa Collector name is identified by:
- org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.datacollection.collector.CollectorStub
UNIX Processes For Chukwa Data Processes
Chukwa Data Processors are identified by:
- org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.extraction.demux.Demux
- org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.extraction.database.DatabaseLoader
- org.apache.hadoop.chukwa.extraction.archive.ChukwaArchiveBuilder
The processes are scheduled execution, therefore they are not always visible from the process list.
Checks for MySQL Replication
At slave server, MySQL prompt, run:
show slave status\G
Make sure both Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both "Yes".
Things to check if MySQL replication fails:
- Make sure grant permission has been enabled on master MySQL server.
- Check disk space availability.
- Check Error status in slave status.
To reset MySQL replication, run these commands on MySQL:
STOP SLAVE; CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='hostname', MASTER_USER='username', MASTER_PASSWORD='password', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_LOG_FILE='master2-bin.001', MASTER_LOG_POS=4, MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10; START SLAVE;
Checks For Disk Full
If anything is wrong, use /etc/init.d/chukwa-agent and CHUKWA_HOME/tools/init.d/chukwa-system-metrics stop to shutdown Chukwa. Look at agent.log and collector.log file to determine the problems.
The most common problem is the log files are growing unbounded. Set up a cron job to remove old log files:
0 12 * * * CHUKWA_HOME/tools/expiration.sh 10 !CHUKWA_HOME/var/log nowait
This will set up the log file expiration for CHUKWA_HOME/var/log for log files older than 10 days.
Emergency Shutdown Procedure
If the system is not functioning properly and you cannot find an answer in the Administration Guide, execute the kill command. The current state of the java process will be written to the log files. You can analyze these files to determine the cause of the problem.
kill -3 <pid>


